-
Call
-
-
Address
Gat No 261, Moshi -Alandi Rd,
Moshi, Pune-412105
Heat Exchangers
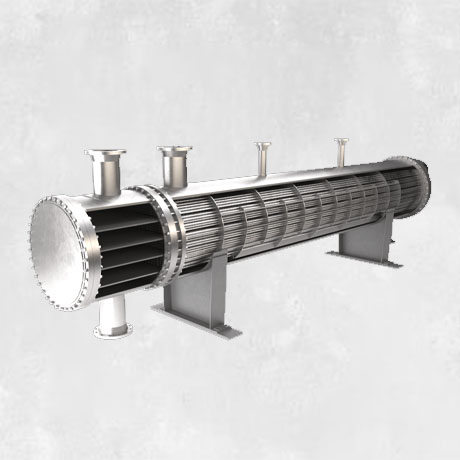
Heat Exchangers
A heat exchanger is a piece of equipment that continually transfers heat from one
medium to another in order to carry process energy.
Heat exchangers are used to transfer heat between two sources. The exchange can
take place between a process stream and a utility stream (cold water, pressurized steam,
etc), a process stream and a power source (electric heat), or between two process streams
resulting in energy integration and reduction of external heat sources. Typically, a heat
exchanger is used with two process streams.
The term heat exchanger applies to all equipment used to transfer heat between two
streams. However, the term is commonly used to equipment in which two process streams
exchange heat with each other. In the other hand, the term heater or cooler is used when
the exchange occurs between a process stream and a plant service stream. Exchangers can
also be classified as fired (heat source is fuel combustion) and unfired exchangers.
Design Standard : TEMA (Tubular Exchanger Manufacturers Association)
There are many types of heat exchangers applied in the process industry. These types include :
- Shell and Tube Exchangers
- Plate-fin Exchangers
- Spiral Heat Exchangers
- Air Coolers and Condensers
- Hairpin / Double Pipe Exchangers
- Fired Heaters
